elisa test overview|elisa test explained : white label There are several variations of an ELISA test depending on whether it’s checking for antibodies or antigens. An example of checking for antibodies can give . See more The Lexa sterilizer helps protect patients, mitigate risk, and achieve sterilization best practices. With its patented steam-condensing vacuum technology, coupled with closed-door vacuum drying, Lexa produces sterile, bone-dry loads.
{plog:ftitle_list}
We custom design and build all of our ASME certified autoclaves to fit your needs. Above all .
ELISA is a common laboratory testing technique that detects and counts certain antibodies, antigens, proteins and hormones in bodily fluid samples. This includes blood, plasma, pee, saliva (spit) and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). “ELISA” stands for “enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay.” Another name for it is . See moreSeveral medical tests involve the use of the ELISA technique. But it’s important to note that your laboratory test results won’t say “ELISA test.” This is because . See moreThere are several variations of an ELISA test depending on whether it’s checking for antibodies or antigens. An example of checking for antibodies can give . See moreThe results of ELISA vary based on what it’s testing and the laboratory that processed the test. Many ELISA tests have a positive or negative result, but some . See more
If your test results are abnormal, it doesn’t necessarily mean that you have a medical condition. An error in the collection, transport or processing of the test . See moreELISA (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay) is a plate-based assay technique designed for detecting and quantifying soluble substances such as peptides, proteins, antibodies, and hormones. Other names, such as enzyme .
ELISA test results, what does a positive ELISA test tell you? ELISA results may be interpreted quantitatively, qualitatively or semi-quantitatively. In a quantitative assay, a serial dilution of a known standard is .The ELISA method has many variations, all of which rely on complex of an antigen and an antibody/enzyme conjugate. Signal is generated by turnover of substrate. . In most cases, sandwich assays are more specific because the assay requires 2 antibodies to recognize the target of interest. CST offers ELISA kits where optimal antibody pairs have .
elisa kit insert
Enzyme Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) is a very sensitive immunochemical technique which is used to access the presence of specific protein (antigen or antibody) in the given sample and it’s quantification.Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) is an immunological technique extensively used in research and clinical laboratory settings to quantitatively identify a specific protein (i.e., the antigen or biomarker) in a biological matrix while relying on the principle of the specific binding interaction between the antigen and the antibody against the antigen of interest .The most widely used ELISA assay format is the sandwich ELISA assay, which indirectly immobilizes and indirectly detects the presence of the target antigen. This type of capture assay is called a “sandwich” assay because the analyte to be measured is bound between two primary antibodies, each detecting a different epitope of the antigen .Fig. 9.7. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISA). The assay substrate consists of protein or peptide targets that are overexpressed, purified, and coated on to plastic wells, usually at 1–10 μg/mL (A).Antibodies in patient serum or cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) that bind to the target are detected with an anti-human secondary antibody (Ab) that is linked to an enzyme, usually .
ELISA is the basic assay technique, known as enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (also referred to as EIA: Enzyme Immunoassay) that is carried out to detect and measure antibodies, hormones, peptides and proteins in the blood. Antibodies are blood proteins produced in response to a specific antigen. It helps to examine the presence of antibodies .Several medical tests involve the use of the ELISA technique. But it’s important to note that your laboratory test results won’t say “ELISA test.” This is because ELISA is a laboratory technique, and there are countless variations of the tests that use it. One common use of the ELISA technique is to detect and measure antibodies, including:Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) is an immunological assay widely used in basic science research, clinical application studies, and diagnostics. The ELISA . Contact Us. . Overview | DOI: 10.1007/978-1-0716-2903-1_1. Affiliations: Wayne State University, School of Medicine, Detroit, MI, USA; Marshall B. Ketchum University, Fullerton .The most widely used ELISA assay format is the sandwich ELISA assay, which indirectly immobilizes and indirectly detects the presence of the target antigen. This type of capture assay is called a “sandwich” assay because the analyte to be measured is bound between two primary antibodies, each detecting a different epitope of the antigen .
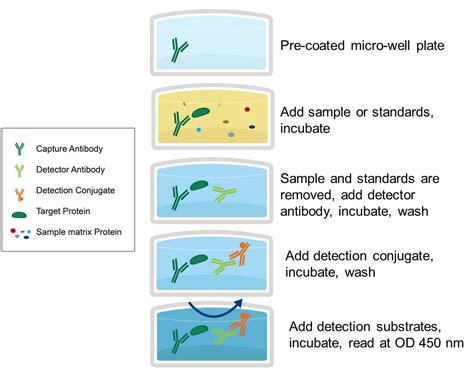
Direct ELISA: The unknown sample containing the antigen of interest is adhered directly to the well, followed by detection with a primary antibody. Indirect ELISA: Begins the same way as a Direct ELISA, but the primary antibody is not linked with the enzyme and a secondary antibody must be used for detection. Sandwich ELISA (Figure 1)
The most widely used ELISA assay format is the sandwich ELISA assay, which indirectly immobilizes and indirectly detects the presence of the target antigen. This type of capture assay is called a “sandwich” assay because the analyte to be measured is bound between two primary antibodies, each detecting a different epitope of the antigen .
The most widely used ELISA assay format is the sandwich ELISA assay, which indirectly immobilizes and indirectly detects the presence of the target antigen. This type of capture assay is called a “sandwich” assay because the analyte to be measured is bound between two primary antibodies, each detecting a different epitope of the antigen .The enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) is a powerful method for detecting and quantifying a specific protein in a complex mixture. Originally described by Engvall and Perlmann (1971), the method enables analysis of protein samples immobilized in microplate wells using specific antibodies. The technique has revolutionized immunology and . This short animation demonstrates enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) to measure specific antibodies. This resource was developed by Cary Engleberg of . Enzyme immunoassays (EIAs) use the catalytic properties of enzymes to detect and quantify immunologic reactions. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) is a heterogeneous EIA technique used in clinical analyses. In this type of assay, one of the reaction components is nonspecifically adsorbed or .
The most widely used ELISA assay format is the sandwich ELISA assay, which indirectly immobilizes and indirectly detects the presence of the target antigen. This type of capture assay is called a “sandwich” assay because the analyte to be measured is bound between two primary antibodies, each detecting a different epitope of the antigen .
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) is one of the most specific and straightforward assays for detecting biomolecules in research and clinics. With advances in analytical methods, ELISA assay has been constantly optimized to improve its sensitivity, and different types of ELISA are now availab .ELISA stands for Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay. It's a widely adopted laboratory method used for detecting and quantifying substances such as proteins, peptides, antibodies, and hormones. The method involves coating a plate with a specific antigen or antibody, followed by a series of reactions that produce a measurable signal, often a color . The ELISA test is a medical test that measures your blood’s antibodies. Learn about how it can help you get better medical treatment, what to expect, and more.
An enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, also called ELISA or EIA, is a test that detects and measures antibodies in your blood.This test can be used to determine if you have antibodies related to .
The most widely used ELISA assay format is the sandwich ELISA assay, which indirectly immobilizes and indirectly detects the presence of the target antigen. This type of capture assay is called a “sandwich” assay because the analyte to be measured is bound between two primary antibodies, each detecting a different epitope of the antigen .Indirect ELISA Assay. While similar to a direct ELISA, the indirect ELISA detects the binding antibody using a second, conjugated antibody. In general, the first few steps of a direct ELISA are followed, including immobilization and blocking. A detection antibody is added but, unlike the direct ELISA, this antibody is not conjugated.
The most widely used ELISA assay format is the sandwich ELISA assay, which indirectly immobilizes and indirectly detects the presence of the target antigen. This type of capture assay is called a “sandwich” assay because the analyte to be measured is bound between two primary antibodies, each detecting a different epitope of the antigen .Qualitative ELISA Test Results. Qualitative analysis of ELISA determines the presence or absence of the target analyte and is used when research calls for just a positive or negative signal. The presence of the analyte can be determined by observing any signal compared to a blank sample or a negative control.The most widely used ELISA assay format is the sandwich ELISA assay, which indirectly immobilizes and indirectly detects the presence of the target antigen. This type of capture assay is called a “sandwich” assay because the analyte to be measured is bound between two primary antibodies, each detecting a different epitope of the antigen .
The main objective of this review is to present an overview of the historical journey that had led to the invention of EIA/ELISA, an indispensible method for medical and research laboratories, types of ELISA developed after its invention [direct (the first ELISA method invented), indirect, sandwich and competitive methods], problems encountered .
enzyme linked immunosorbent assay test

3.1 The autoclave expansion test provides an index of potential delayed expansion caused by the hydration of CaO, or MgO, or both, when present in portland cement. 3
elisa test overview|elisa test explained